Electronic excitation-induced semiconductor-to-metal transition in monolayer MoTe₂
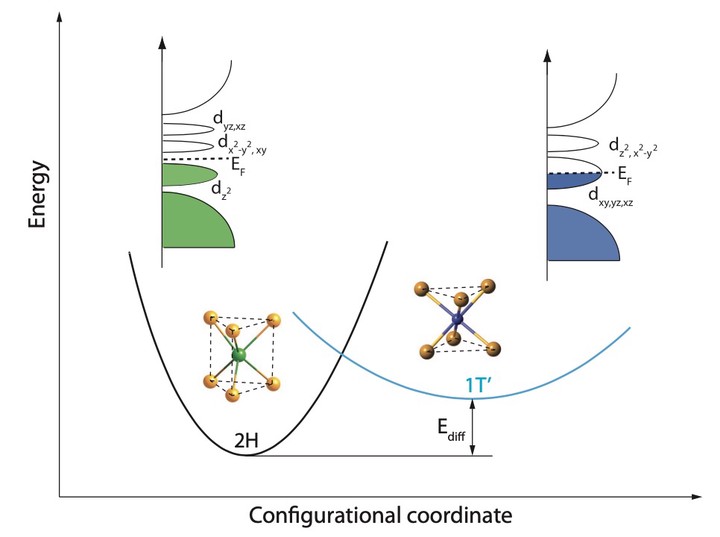 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
Reversible polymorphism of monolayer transition-metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) has currently attracted much attention from both academic and applied perspectives. Of special interest is MoTe2, where the stable semiconducting 2H and metastable (semi)metallic 1T’ phases have a rather small energy difference implying the low-energy cost of such a transition. In this work, using first-principles calculations, we demonstrate that there exists a previously unknown phase of MoTe2, namely a distorted trigonal prismatic phase with alternating shorter and longer bonds and bond angles, that is formed in the electronically excited state due to population inversion. This phase, which is unstable and decays to the ground 2H state after cessation of the excitation, is metallic and can act to lower the energy barrier on the way to the metastable 1T’ phase. Our findings indicate that there exists a previously unexplored route of ultrafast local and selective band-structure control in monolayer TMDC using electronic excitation, which will significantly broaden the application spectrum of these materials.